In December 2016, the IEEE Transactions on Power Systems published the paper “Laboratory Education of Modern Power Systems using PHIL Simulation” by P. Kotsampopoulos, V. Kleftakis, N. Hatziargyriou of Smart Grids Research Unit, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National Technical University of Athens.
Published by ERIGrid as open access, the paper exemplifies the first-time systematic use of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL) simulation for laboratory education. Laboratory exercises have been designed on the four selected topics crucial for the understanding of power system operation. These topics focus on the effects of increased integration of Distributed Generation (DG).
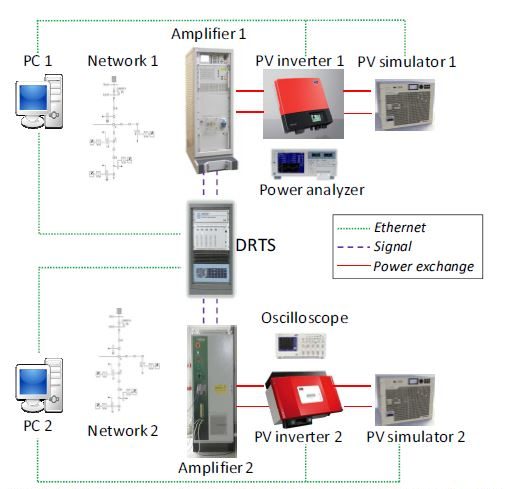
The exercises start with the operation of the traditional power system and gradually incorporate DG related topics that show both benefits and challenges. A hands-on approach is supported by the appropriate lab configuration consisting of two independent PHIL setups.
The assessment of the laboratory exercises by the students is clearly positive underlining the value of PHIL simulation for power system education.
Related:
ERIGrid papers, reports, publications
NTUA’s infrastructure in Transnational Access
